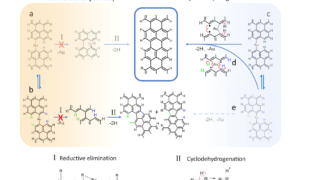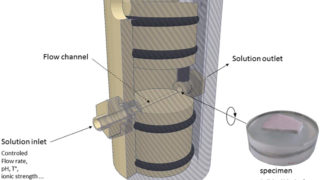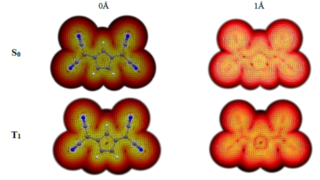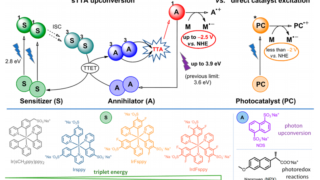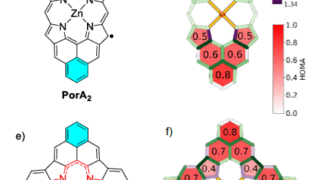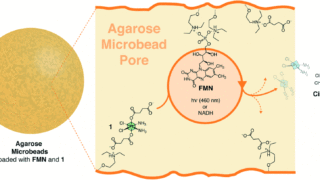
A hydrogel matrix as viable solution for the efficient catalytic activation and delivery of cisplatin
Catalysis-based approaches for the activation of anticancer rely on the use of metal catalysts capable of deprotecting inactive precursors of organic drugs or transforming key biomolecules available in the cellular environment. Nevertheless, the efficiency of most of the schemes described so far is rather low, limiting the benefits of catalytic amplification as a strategy for […]