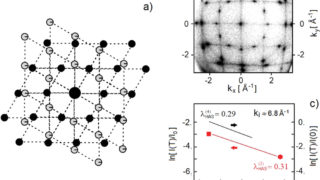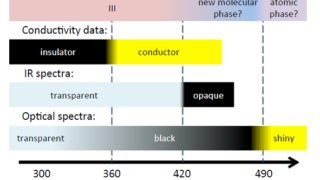
Black metallic hydrogen due to proton quantum fluctuations
The most famous conjecture in condensed-matter physics was proposed in 1935, when Hillard Huntington and Eugene Wigner calculated the properties of hydrogen squeezed to high density and pressure. They predicted that under pressures above 25 gigapascals (GPa), hydrogen would undergo a density-driven transition from an insulating, molecular solid to a conducting, atomic solid . In […]