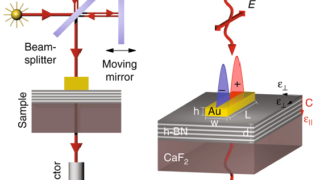
Using an optical antenna to launch phonon polaritons in a low-dimensional van der Waals crystal
Condensed matter • Materials • Nanotechnology • Quantum physics
The so-called van der Waals materials consist of two-dimensional layers bound by weak van der Waals forces. After the isolation of graphene, the field of two-dimensional van der Waals materials has experienced an explosive growth and new families of two-dimensional systems and block-layered bulk materials have been created. This growth has been fueled mainly by […]