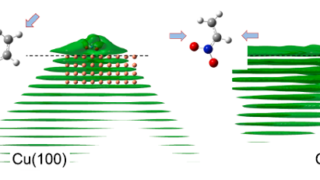
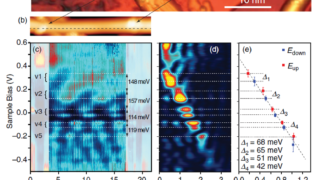
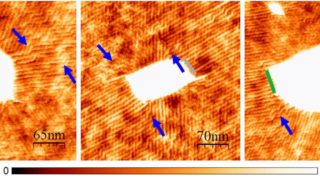
Topological graphene nanoribbons
In the last decades, a mathematical description of symmetries in nature called topology has been applied to describe and predict new electronic and magnetic properties of materials. A very simple aspect of topology connects a symmetry in the atomic structure of a crystal with a class of materials. Many materials that we know or use […]