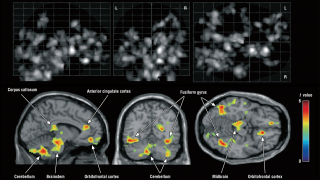
Microglia and autism
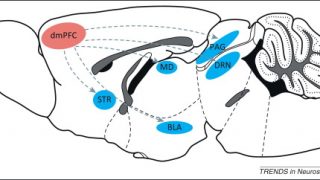
Microglial cells are the immune cells that reside in the central nervous system. They have phagocytic capacity, constitute 10% of the cells of the brain and form a fairly regular three-dimensional network in which each microglia has a unique territory. Its cell body presents many expansions with numerous fine processes, amazingly mobile, with which they […]