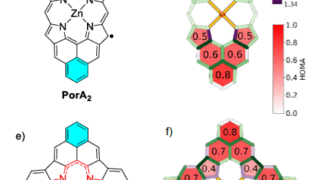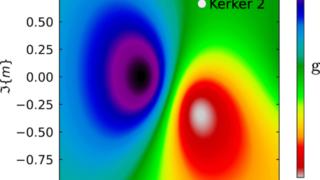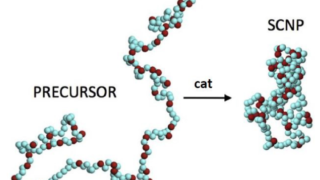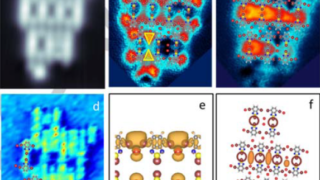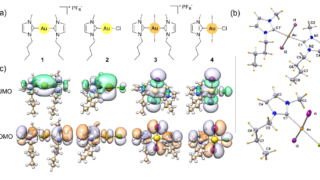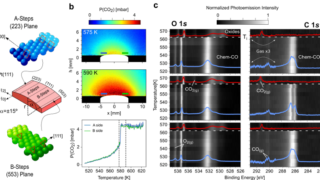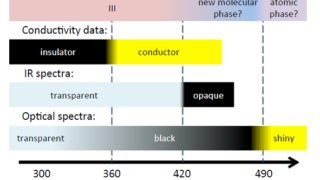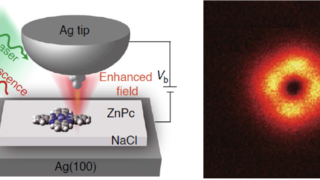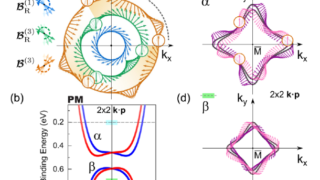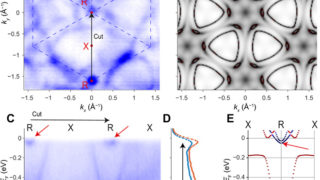
Pyrite CoS2 is shown to be a magnetic Weyl semimetal
Back in 1929, theoretical physicist Hermann Weyl predicted the existence of a new elementary particle with intriguing properties. Specifically, it would be massless (like a photon), have half-integer spin (like an electron) and exist in two mirror-image versions (like left- and right-handed gloves)—a property known as chirality. Imagine there exist a material in which an […]