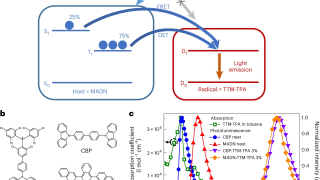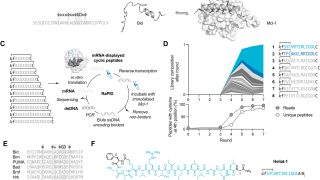
Helix-focused peptide libraries for de novo inhibitor discovery
Chemistry • DIPC Biochemistry • DIPC Computational and Theoretical Chemistry
Protein molecules consist of one or several long chains of aminoacids (usually between and 300 units) called polypeptides – a peptide is an organic compound comprising two or mores aminoacids – linked in a characteristic sequence. This sequence is called the primary structure of the protein. These polypeptides may undergo coiling or pleating, the nature […]